Manual for CCMOP
Here we give a brief manual for using CCMOP. There are three parts. The first part is the manual for installing and running the docker image of CCMOP. The second part is the usage of the transparent compilation script wac. The final part is a brief account of the syntax of the property.
1.Install and Run the Docker Image
(1).Install and start docker
We suppose you have installed the docker environment; otherwise, please go to this link for help.
(2).Download CCMOP docker image
The following command will download the image named ccmop/ccmop.
docker pull ccmop/ccmop
If the image downloading succeeds, you can use the following command to check.
docker images
You should see that an image named ccmop/ccmop exists.
(3).Run the docker image
You can run the docker image and have a try. The following command will create a container for ccmop/ccmop and open the terminal.
docker run -it ccmop/ccmop /bin/bash
Get in the CCMOP/examples/CXX/UnSafeIterator directory and compile an example program.
cd CCMOP/examples/CXX/UnSafeIterator
wac -cxx -mop UnSafeIterator.mop test.cpp -o a
./a
If the commands above succeed, you can see the results in bash.
NOTE: If you use CCMOP not in our supplied docker image, you should run the following commands to initialize the environmental variables, and the clang version should be 15.02 with Release type.
- Exports required binary and library path.
export PATH=$PATH:<The bin of CCMOP> export ASPECT_LIB=<The lib of CCMOP> - Install the script of wac, in directory wcompiler
python3 setup.py install
2.Usage of wac
We show the usage of wac as follows.
(1). Common arguments
The following command will list all the arguments.
wac -h
The argument -print will dump the instrumented file.
wac -print
(2). Compile model
There are two models of WAC, one for project compilation and another for single-file compilation.
- for single-file compilation:
- Using the argument -cxx will inform the compiler that the current file is to be compiled as a C++ file.
- The argument -mop specifies the input property’s path.
- The contents of Clang compile arguments are the arguments that Clang supports.
wac [-cxx] [-print] -mop <A property file> <Clang compile arguments>
- for project compilation:
- Using the argument -proj will turn the compiling model into project compilation.
wac [-print] -proj <The path of configure JSON.>The configure JSON contains the required information, as shown below.
{ "project_name":"", "compile_language": "", "project_root_dir":"", "mop_file":"", "project_build_subdir":"", "project_compile_cmd":"" }
- Using the argument -proj will turn the compiling model into project compilation.
- project_name is the name of the target project.
- compile_language could be c or cxx, which is the language of the target project.
- project_root_dir means the path of the root path of the target project, which could be an absolute path or a path related to configure JSON.
- mop_file represents the path of a property, which could be an absolute path or a path related to configure JSON.
- project_build_subdir means the build directory that is often used in CMake.
- project_compile_cmd represents the command to compile the target project; if there are multiple commands, please use ; to split.
Note: if you need to run CMake for the C program, you may need to add the following argument
-DCMAKE_C_COMPILER_ID=Clang
Note: if you need to monitor a program that only generates a static library, you may need to explicitly specify AR as ${war}.
3.Property Syntax
The syntax of the property is designed based on JavaMOP’s MOP syntax. We show the property syntax (not AOP syntax) with a file extension as .mop. The symbol [] represents an optional occurrence (either once or none), while the symbol {} represents a repeating occurrence (either once or multiple times).
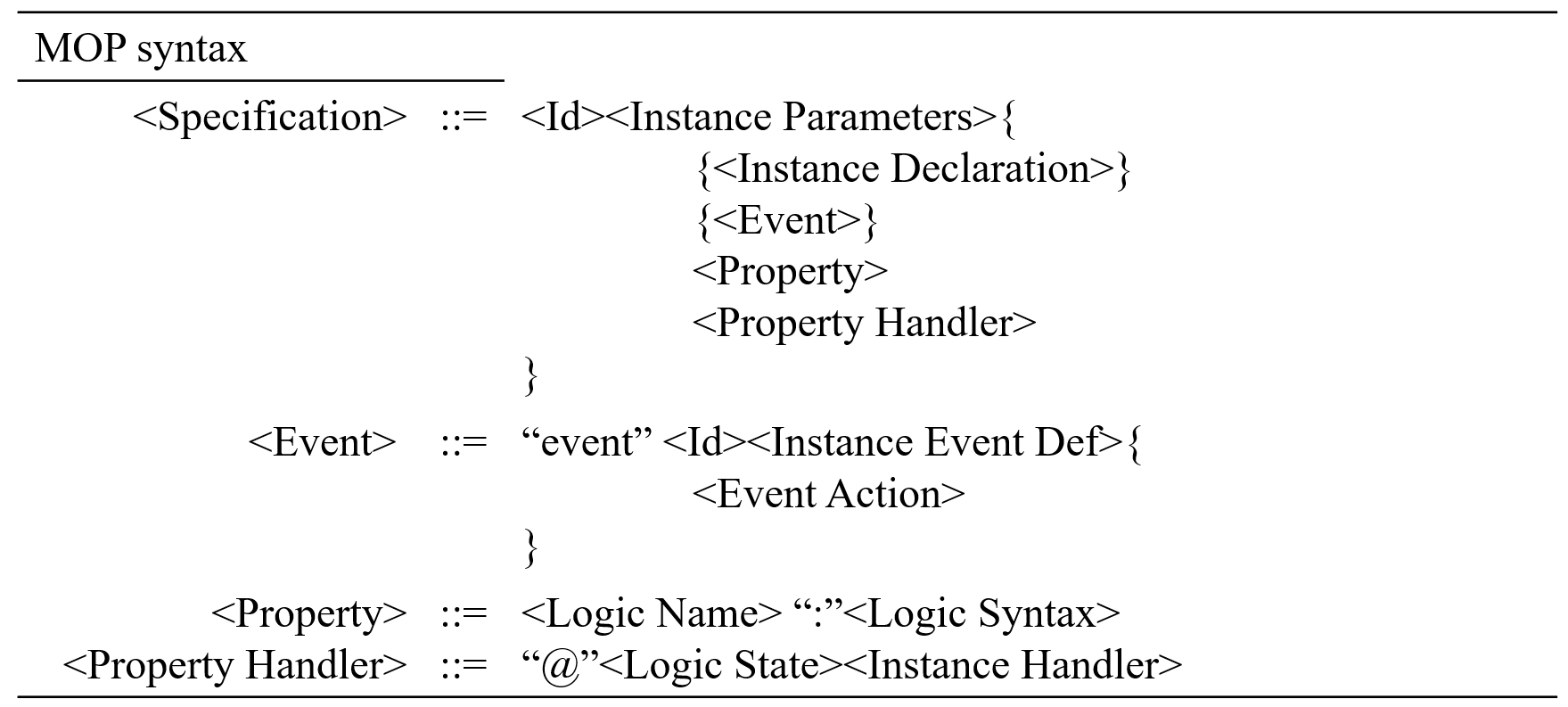
(1). MOP syntax
The MOP syntax describes the top syntax of the property.
- Specification is the main entity of MOP.
- Event is the essential component of Specification.
- Property is a logic expression that describes the behavior of event streams.
- Logic Name could be ere or fsm, which is the lanaguage for specifying properties.
- Property Handler is the action that the monitor will carry out when reaching a desired state.
(2).Instance syntax
The Instance syntax describes the syntax involved in MOP syntax.
- Instance parameters in Advice are the subset of Specification parameters, representing the current event focus.
- Id in CCMOP Pointcut is mapping to the Instance parameters in Advice.
- args means get the argument of matching pointcut, and the contents of args may be (none, Id), which means get the second argument from pointcut.
- result means getting the matching pointcut’s return value.
- target means getting the object that owns the matching pointcut.
- within limits the mathching scope by Space Declaration.
- call matches the call sites which the callee functions that conform to the Function Declaration.
- expr matches the new, delete and construct call sites that conform to Expr Declaration.
- derefPointer matches all the site of dereferencing pointers that conforms to the pointer type.
- endProgram mathces all the exits of prgrams including return statement in main function and exit callsites.
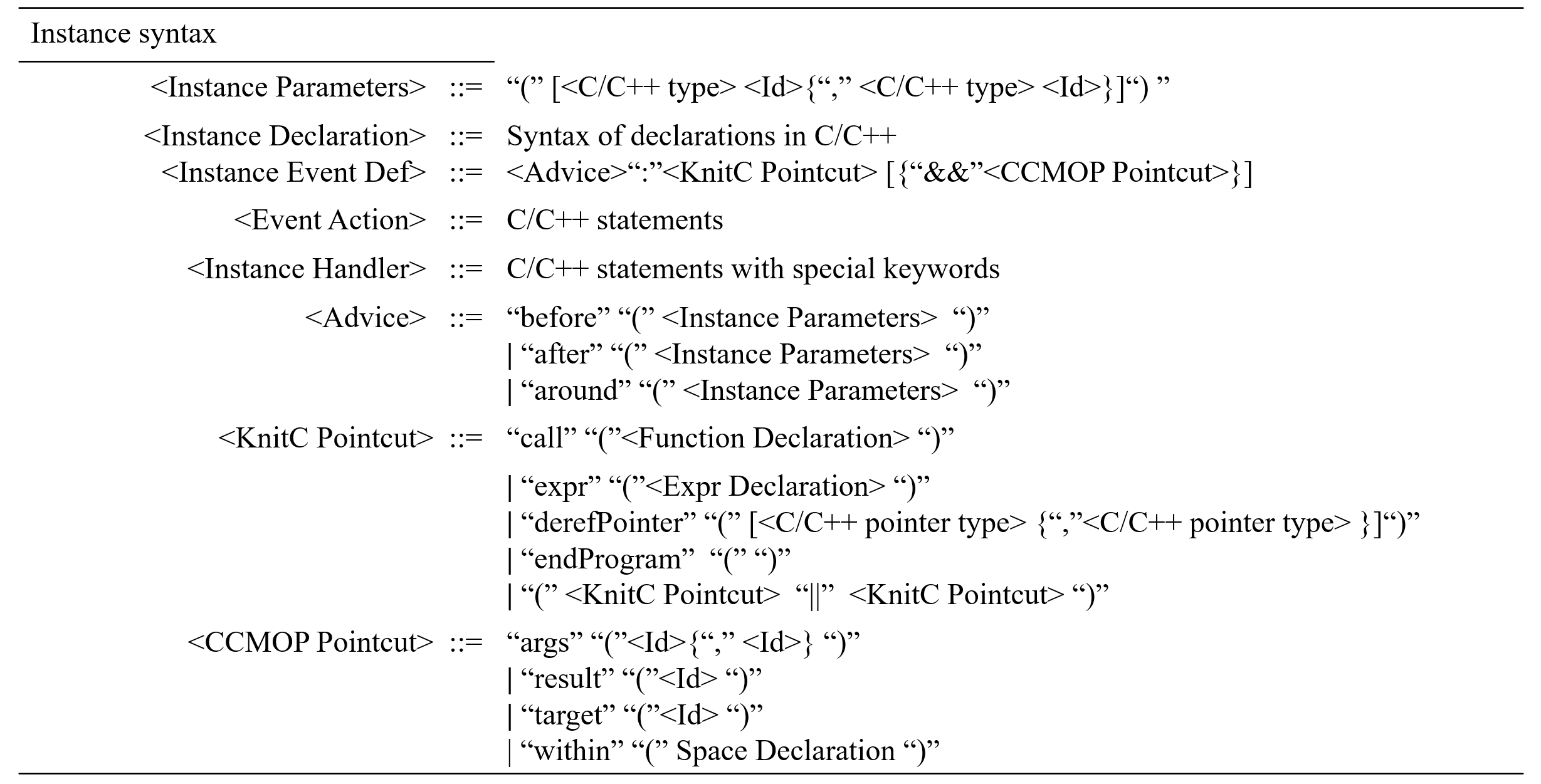
By the way, when derefPointer encounters situations where code instrumentation may alter the program semantics, we ignore such instrumentations.
(3).AOP syntax
The following syntax describes the core feature of our AOP language designed for C++ programs.
- % in Function Declaration means that this declaration does not focus on the return type.
- … in Function Declaration and Expr Declaration means that the declaration does not focus on the args.
- * in Expr Declaration and Expr Name means this declaration does not focus on the specified type of Expr.
- Scoped Type represents the C++ type with namespace and * are the pointer symbol.
- Space Declaration represents either namespace scope or function scope. If ( ) appears at the end of Space Declaration, the final scope is function scope; otherwise, it is namespace scope.
- Special Keywords contains __RESET, TARGET and LOC.
- _RESET means resetting the current monitor’s state.
- TARGET means the current monitor, which is generally used in dumping the monitor member information.
- LOC means the location of the current event occurs.

Contacts
Please feel free to contact us if you have any questions about CCMOP.
- Yongchao Xing (xingyc0979@nudt.edu.cn)
- Zhenbang Chen (zbchen@nudt.edu.cn)